As the world becomes increasingly digitized, the terms “digital sovereignty” and “data sovereignty” are becoming more common. However, many people are still unsure about the difference between these two concepts. In this article, we will explore the meaning of each term and discuss why they are important for businesses and individuals alike.
What is Digital Sovereignty?
Digital sovereignty refers to an organization’s ability to govern the digital technologies used within it. This includes the power to regulate the use of data and the internet, as well as the ability to control access to digital infrastructure.
The concept of digital sovereignty has become increasingly important in recent years, as governments have sought to protect their citizens from cyber threats and safeguard their economies from foreign interference. Some countries have even gone so far as to create their own digital ecosystems, with their own tech giants and internet protocols, in order to maintain control over their digital infrastructure.
If you want to learn more about how to navigate the complex world of digital sovereignty, read our 6 Pillars of Digital Sovereignty
What is Data Sovereignty?
Data sovereignty, on the other hand, refers to the idea that data is subject to the laws and governance of the country in which it is collected or stored. This means that if a company collects data in one country, it must comply with the data protection laws of that country, even if it stores the data in another country.
Data sovereignty is important because it helps to protect the privacy of individuals and the security of sensitive information. It also ensures that countries have the power to regulate the flow of data within their borders and prevent other countries from accessing their citizens’ data without permission.
To learn more about data sovereignty and its importance, explore our article Why Data Sovereignty Should Matter to Us All.
Digital Sovereignty vs Data Sovereignty: What’s the Difference?
While digital sovereignty and data sovereignty are related concepts, they are not the same thing. Digital sovereignty refers to the ability to govern the digital infrastructure, while data sovereignty refers to the laws and governance surrounding the collection and storage of data.
Data sovereignty is about control, while digital sovereignty is about ownership. An organization may have sovereignty over its digital data, but it may not have digital sovereignty over the infrastructure and technology used to collect and store information.
To facilitate comprehension of the upcoming section, it is crucial to outline the key points that distinguish digital sovereignty from data sovereignty. Therefore, let us compile the relevant factors once more:
- Digital sovereignty and data sovereignty are related but not the same thing.
- Digital sovereignty refers to governing digital infrastructure, while data sovereignty refers to laws and governance surrounding data collection and storage.
- Data sovereignty is about control, while digital sovereignty is about ownership.
- An organization may have sovereignty over its data, but not over the infrastructure and technology used to collect and store it.
By exploring connections between digital sovereignty and data sovereignty, we can gain a better understanding of their individual roles. Let’s delve deeper into this topic.
The Connection Between Digital Sovereignty and Data Sovereignty
Digital sovereignty and data sovereignty have gained importance in the context of global digitalization. As explained, digital sovereignty refers to the control and ownership of digital infrastructure including the internet, telecommunications networks, and digital platforms and services. Data sovereignty, on the other hand, refers to controlling and regulating the flow of data within an organization, including personal data, financial data, and other sensitive information.
The two concepts are connected in that digital sovereignty is necessary for an organization to exercise data sovereignty. Without control over its digital infrastructure, an organization cannot effectively regulate the flow of data within its borders. For example, if a foreign company controls an organization’s digital infrastructure, that company may be able to access and exploit sensitive data without the organization’s knowledge or consent.
In the context of a country, the same holds true. In fact, data sovereignty is essential for a country to maintain digital sovereignty. Without the power to regulate the flow of data within its borders, a country could struggle to safeguard its digital infrastructure against cyber threats and other security risks.
Digital sovereignty is not just about data, it also encompasses the infrastructure and technologies that are necessary to handle and process data. This includes the internet, telecommunications networks, digital platforms, and other tools that are essential for an organization to function in the digital age. Without control over these technologies, an organization may be unable to protect its digital infrastructure from cyber threats or regulate the flow of data within it.
In this sense, digital sovereignty encompasses both data sovereignty and technological sovereignty. Technological sovereignty refers to an organization’s ability to develop and control its own technologies, rather than relying on foreign technologies that may be subject to external influence or control. By developing its own technologies, an organization can ensure that it has the tools necessary to protect its digital infrastructure and regulate the flow of data within it, without being dependent on external actors.
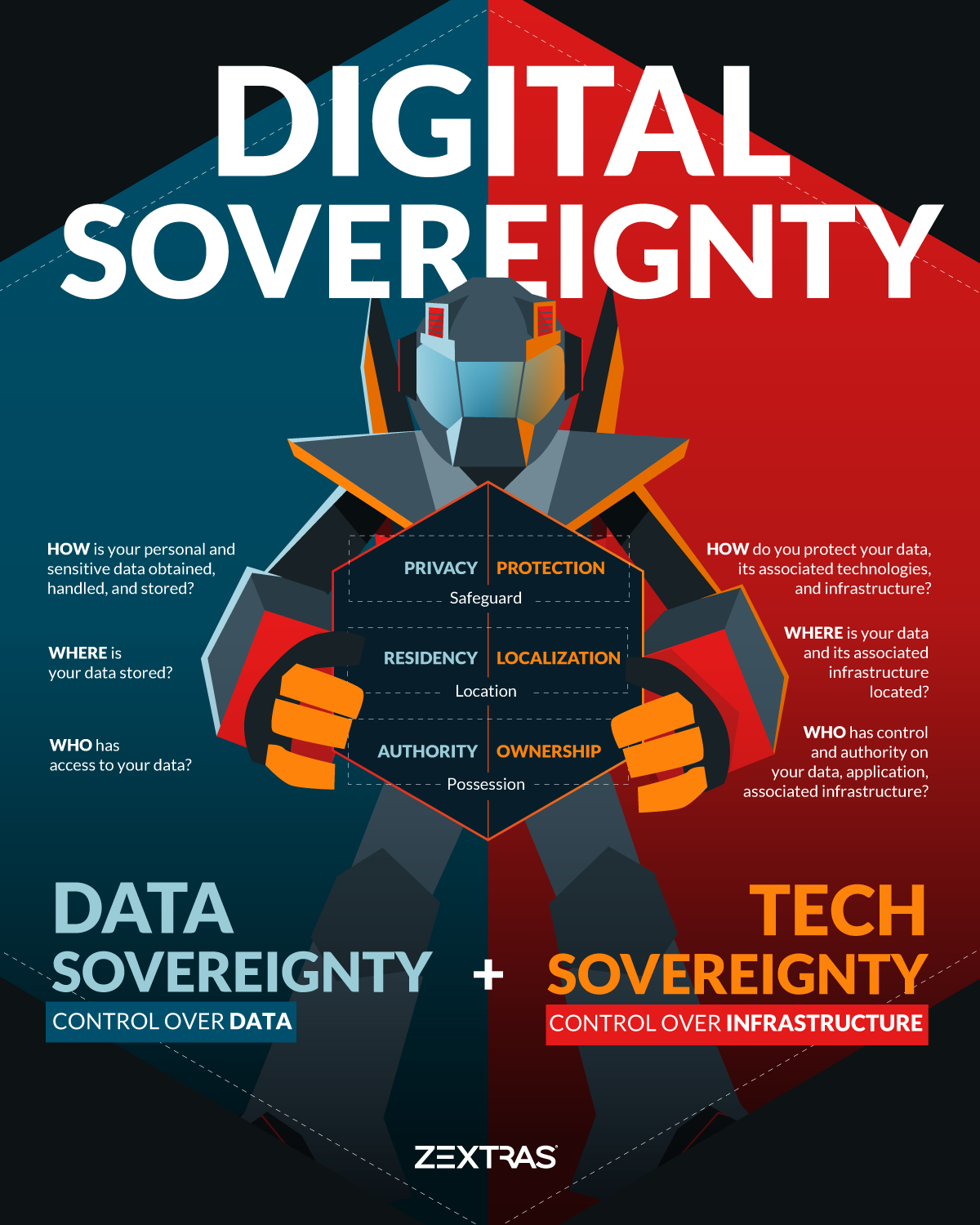
By familiarizing yourself with the 6 pillars of digital sovereignty, you can discern the relationship between digital sovereignty and data sovereignty in the accompanying diagram. The diagram illustrates that privacy, residency, and authority are closely linked to data sovereignty, whereas protection, locality, and ownership are tied to technological sovereignty. When these six pillars are combined, they form what is known as digital sovereignty.
Hyperscale cloud providers have recently been making efforts to address some of these 6 pillars in their solutions and services, though they do not always succeed.
Why Is Digital Sovereignty Important and Why Should It Matter to You?
Digital sovereignty and data sovereignty help to ensure that an organization or the whole country has the power to regulate its own digital infrastructure and protect the privacy and security of its employees’ or citizens’ data. Without these concepts, organizations would be at the mercy of foreign tech companies and governments, which could use their power to access and control sensitive information.
In addition, digital sovereignty and data sovereignty are crucial for businesses that operate across international borders. Companies must comply with the data protection laws of every country in which they operate, which can be a complex and challenging task. Understanding the concepts of digital sovereignty and data sovereignty can help businesses to navigate this complex regulatory landscape and avoid costly penalties for non-compliance.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between digital sovereignty and data sovereignty is crucial for businesses and individuals alike, as they will have a significant impact on how we interact with technology in the future.
