- Understanding Public Cloud Risks
- Corporate Data Security at Risk
- Real-World Breaches
- Hidden Data Protection Challenges
- Cloud Solutions Benefits – But at What Cost?
- The Cost of Downtime
- Data Sovereignty and Compliance Risks
- The Cost Risks of Public Cloud
- Vendor Risk and Trust Management
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Security Strategies
- Best Practices for Cloud Security
- Conclusion
The adoption of cloud services has skyrocketed, with over 94% of enterprises leveraging some form of cloud computing. Public cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer compelling benefits: scalability, speed, and cost efficiency. However, this rapid shift has introduced a new wave of challenges.
A 2024 ISC² report shows that 43% of companies experienced a cloud-related security incident in the past 12 months.
As cloud reliance grows, so do public cloud risks, including cloud vulnerabilities, compliance hurdles, and vendor management issues. This article explores the expanding landscape of risks and how organizations can respond to ensure corporate data security.
Understanding Public Cloud Risks
Public cloud platforms operate on a shared responsibility model, often misunderstood by enterprise users. While the provider secures the infrastructure, businesses are responsible for securing their own data and configurations.
Key Cloud Threats:
- Misconfigured Storage Buckets
- Insecure APIs
- Insider Threats
- Inadequate Access Controls
These lead to various cloud security issues, such as data exfiltration and cloud information breaches.
Corporate Data Security at Risk
Sensitive information, customer data, proprietary algorithms, and financial records are increasingly stored on public clouds. Yet these assets are often insufficiently protected.
Real-World Breaches
| Incident | Provider | Affected Data | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital One (2019) | AWS | 106M customer records | $80M regulatory fine |
| Facebook (2021) | Unknown | 533M phone numbers | GDPR investigations |
| Accenture (2021) | Azure | Internal credentials | Operational risk exposure |
Organizations must rethink business data protection in light of these data compromise events.
Hidden Data Protection Challenges
Cloud environments present unique data safeguarding difficulties that traditional systems did not.
Top 5 Data Protection Challenges:
- Unclear Encryption Ownership
- Weak Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Shadow IT and Unmanaged Apps
- Data Residency Conflicts
- Delayed Incident Detection
Cloud Solutions Benefits – But at What Cost?
Yes, cloud services offer agility, global reach, and cost savings. But unchecked usage leads to unexpected problems.
Benefits vs. Risk Tradeoffs
| Cloud Advantage | Hidden Risk |
|---|---|
| Elastic storage | Egress fee spikes |
| Quick deployment | Misconfiguration exposure |
| Global scalability | Jurisdictional data exposure |
The Myth of Infinite Availability: Impact of Cloud Outages
Even top-tier providers suffer outages. In Dec 2023, AWS experienced a 7-hour East Coast outage, affecting thousands of businesses.
The Cost of Downtime
- $300,000/hour loss for large enterprises (Gartner)
- 74% of businesses experienced moderate to high disruption
Data Sovereignty and Compliance Risks
Cloud users often lack clarity on where their data resides—this is a growing legal concern.
Jurisdictional Risks:
- U.S. CLOUD Act vs. EU’s GDPR
- Schrems II ruling invalidating Privacy Shield
- Local data laws in China, Russia, and Brazil
| Region | Key Regulation | Risk if Violated |
|---|---|---|
| EU | GDPR | €20M or 4% of global turnover |
| USA | HIPAA/FERPA | Fines + lawsuits |
| Brazil | LGPD | Up to 2% revenue |
The Cost Risks of Public Cloud
Cloud billing models are complex. Overprovisioning, egress charges, and data storage tiers can result in cost overruns.
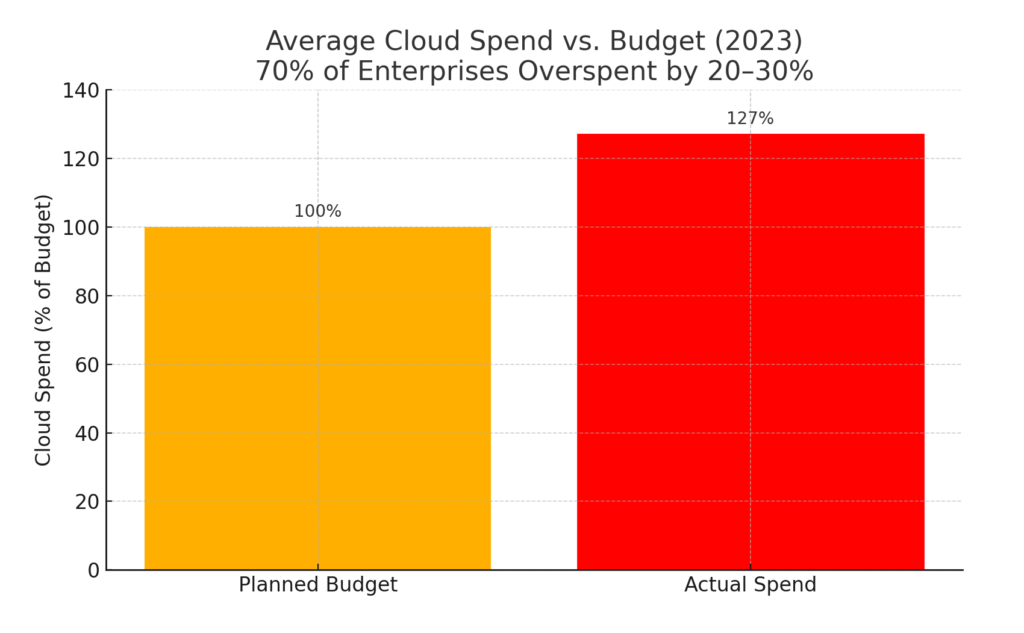
Vendor Risk and Trust Management
Cloud platforms introduce vendor lock-in, SLAs with limited liability, and opaque risk ownership.
Vendor Evaluation Checklist:
- Is data portability supported?
- Are SLAs transparent and enforceable?
- How is incident reporting handled?
- Is the provider compliant with required certifications (ISO, SOC, etc.)?
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Security Strategies
Diversification through multi-cloud or hybrid cloud setups improves resilience but adds complexity.
Best Practices:
- Centralized identity management
- Cloud-native security tools integration
- Data classification and tiered access
- Backup redundancy across clouds
Best Practices for Cloud Security
A solid cloud defense strategy starts with clarity and control.
Cloud Security Guidelines:
- Enable MFA and role-based access control (RBAC)
- Encrypt data in transit and at rest
- Regular security audits and penetration testing
- Use of CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker)
- Incident response planning
| Best Practice | Tool Example |
|---|---|
| IAM | Azure AD, Okta |
| Encryption | AWS KMS, GCP CMEK |
| Monitoring | Datadog, Splunk |
| Frameworks | CIS, NIST 800-53 |
Conclusion
Public cloud platforms are foundational to digital transformation, but they are not without risk. Organizations must go beyond default settings and consider cloud security a board-level concern. Companies can secure their path in the cloud by implementing strategic vendor evaluations, maintaining multi-cloud protection plans, and upholding data safeguarding policies.
Want to dive deeper into protecting business-critical data? Don’t miss our article on Disaster Recovery Planning for Email Systems: Ensuring Business Continuity and Data Resilience.
