For additional guidance, check out our community articles detailing the process of migrating from your current platform to Carbonio CE.
For enterprise-level requirements and advanced features, consider checking out Zextras Carbonio – the all-in-one private digital workplace designed for digital sovereignty trusted by the public sector, telcos, and regulated industries.
After installing Zimbra Collaboration Suite, there are some configurations you may want to set up in order to improve the security of sending emails to other email systems. Phishing and email spam can be very handy tools for hackers to enter your network, opening some malicious attachments even by one user, can jeopardize the whole network security. In this article we introduce three protection routines, Sender Policy Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC). Based on your sent email quantity you can apply one, two, or all of them.
SPF or Sender Policy Framework is an email authentication method that identifies which mail servers are allowed to send emails on behalf of your domain. I can forge an email header to pretend it has been sent from an address on your domain which is called a spoofing attack. SPF record contains information of only mail servers that are allowed to send emails on behalf of your domain and prevents spammers like me from spoofing your domain. It can be done by comparing the SPF record with the mail server information of the sender. If they don’t match, the email will be identified as unauthorized and will send it to spam or reject completely.
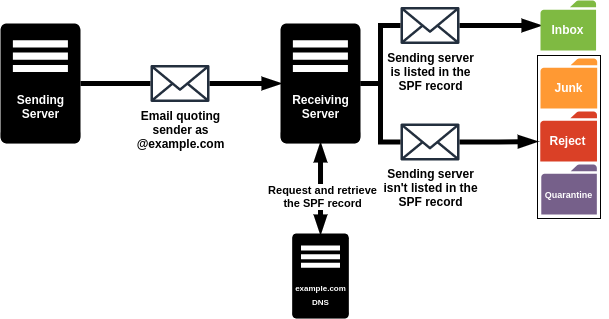
SPF configurations are published in the public Domain Name System (DNS) as TXT records. To configure SPF you should create and add the appropriate record to the public DNS. For the configuration tutorial, you can see the How To Configure Zimbra SPF for Outgoing Emails? and How To Configure Zimbra SPF to Check Incoming Emails?.
DKIM or DomainKeys Identified Mail is an email authentication method that tries to identify email spoofing attempts (creation of email messages with a forged sender address). DKIM enables you as the sender to sign your outgoing email or as a receiver to verify incoming email. It is done with the help of a digital signature, tied to a domain name, for each sent email. This can be verified by looking up the sender’s public key published in the DNS.
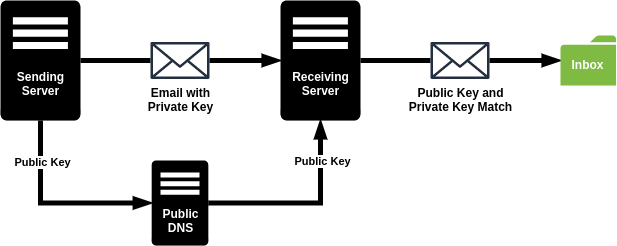
DKIM configurations are published in the public Domain Name System (DNS) as TXT records. To configure DKIM you should create and add the appropriate record to the public DNS. For the configuration tutorial, you can see the How To Configure Zimbra DKIM to Sign Outgoing Emails? and How To Configure Zimbra DKIM to Sign Outgoing Emails?
DMARC or Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance is an email authentication, policy, and reporting protocol that defines how your email servers should manage your SPF and DKIM. DMARC protects your domain from fraudulent emails by allowing you to publish a policy in your DNS records to determine which of DKIM or SPF (or both) should be used for sending emails from your domain.
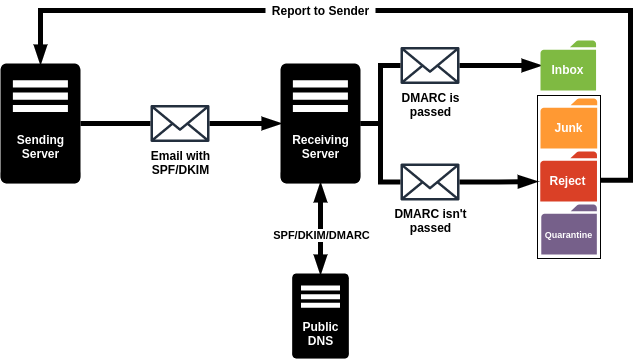
DMARC configurations are published in the public Domain Name System (DNS) as TXT records. To configure DMARC you should create and add the appropriate record to the public DNS. For the configuration tutorial, you can see the How To Configure Zimbra DMARC?.
rDNS or reverse DNS resolves the domain name associated with an IP as opposed to DNS which resolves the IP associated with a domain name. This can be used as an anti-spam technique by verifying the domain name with the help of rDNS to check if it is a dynamically assigned address that is unlikely to be used by a legitimate mail server so some anti-spam policies reject them assuming that emails from these addresses are more likely to spam. Emails which does not identify themselves with a PTR record in an rDNS record will be always rejected by some incoming mail servers.
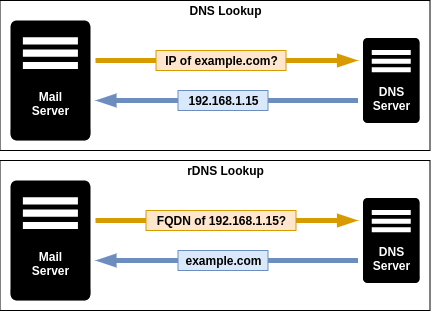
rDNS configurations are published in the public Domain Name System (DNS) as PTR records. To set up rDNS you need first to create the reverse zone domain then add a PTR record to it. For the configuration tutorial, you can see the How To Configure Zimbra rDNS?.

