In today’s digital age, cloud computing has become an integral part of our lives. With the rise of cloud-based services, the issue of digital sovereignty has become increasingly important. Digital sovereignty refers to the ability of individuals and organizations to control their digital data and ensure its protection. Cloud computing, on the other hand, is a technology that allows for the storage, processing, and sharing of data over the internet. While cloud computing has numerous benefits, it also poses challenges to digital sovereignty.
What is Digital Sovereignty And Why Is It Important?
Digital sovereignty refers to the ability of individuals and organizations to control their digital data and their associated infrastructures to ensure its protection. It is the right of individuals and organizations to preserve their data privacy, integrity, and security.
Digital sovereignty is essential because it ensures that individuals and organizations have control over their data and can protect it from unauthorized access, use, and disclosure.
Benefits of Digital Sovereignty
Digital sovereignty is a concept that brings with it a host of benefits for organizations. It also allows nations to exercise control over their digital data, infrastructure, and technologies, promoting innovation and facilitating the development of a domestic digital economy. Benefits of digital sovereignty include the ability to:
- Protect sensitive data from cyber threats and data breaches
- Ensure data privacy and prevent unauthorized access to personal information
- Maintain data integrity and accuracy
- Protect intellectual property rights
- Ensure compliance with data protection regulations and laws
Legal And Regulatory Implications of Digital Sovereignty
Legal implications of digital sovereignty include the need for compliance with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) depending on the location of the organization. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant financial penalties and legal consequences.
Additionally, digital sovereignty is crucial for organizations that handle sensitive data such as healthcare records, financial information, and personally identifiable information (PII) to comply with industry-specific regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
How Does Cloud Computing Impact Digital Sovereignty?
With cloud computing, data is stored in different locations and managed by third-party service providers. While cloud computing offers numerous benefits, it also poses certain challenges to digital sovereignty such as data authority, residency, and ownership.
Generally speaking, cloud computing poses a challenge to achieving every pillar of digital sovereignty. To gain a deeper understanding of how cloud computing impacts digital sovereignty, it is beneficial to examine its influence on each pillar separately.
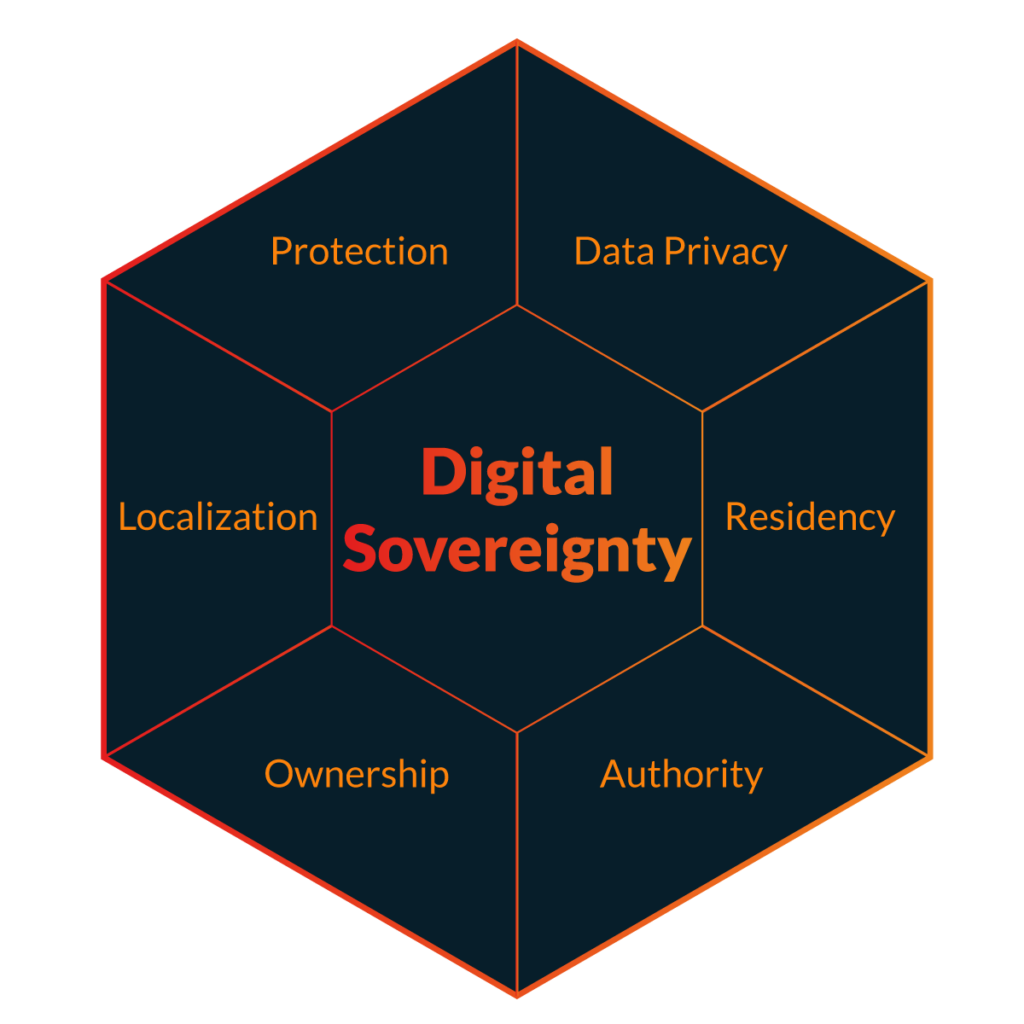
To learn more about these pillars read 6 Pillars of Digital Sovereignty – Importance, Challenges, and How to Achieve Them.
Cloud Computing And Ownership
One significant impact of cloud computing on digital sovereignty is the loss of control over ownership. With cloud-based services, individuals and organizations no longer have complete control over their data as it is stored and the infrastructure is managed by third-party service providers. This makes it challenging for individuals and organizations to ensure the security of their data.
Cloud Computing And Protection
Cloud computing and protection in terms of digital sovereignty can be at odds with each other. While cloud providers may offer security measures to protect data, businesses may not have complete control over these measures. This can make it difficult to ensure that confidential information is not accessed or altered without authorization. Additionally, regular security audits, user access monitoring, and updates to security protocols may not be enough to fully protect against security breaches. Businesses must also consider the risks associated with storing their data in the cloud, such as potential data breaches or unauthorized access by third-party providers.
Cloud Computing And Authority
Cloud computing and authority in terms of digital sovereignty may not go well together either. With cloud computing, businesses may not have complete control over who has access to their information. This can make it difficult to protect sensitive information and ensure that only authorized individuals have access. While cloud providers may offer security measures to protect data, businesses must still trust that the provider is implementing these measures effectively. Additionally, if a cloud provider experiences a security breach, it can be difficult for businesses to know who has accessed their information and take corrective action.
Cloud Computing And Locality
Cloud computing can have negative impacts on obtaining data locality due to the lack of control over where data is physically stored. When businesses store their data in the cloud, they are entrusting a third-party provider with the responsibility of storing and securing their data. This can lead to concerns about data privacy and compliance with local regulations.
Cloud Computing And Residency
Moreover, some countries have strict regulations regarding data residency, requiring that data be stored within their borders. This can be challenging for businesses that operate in multiple countries, as they may need to store data in multiple locations to comply with these regulations. Additionally, if a cloud provider experiences a security breach or data loss, it can be difficult for businesses to recover their data and ensure that it is not accessed by unauthorized parties.
In conclusion, digital sovereignty is a critical concept in today’s digital age, particularly in the context of cloud computing. While cloud computing offers numerous benefits, it also poses challenges to digital sovereignty. The loss of ownership, concerns about data protection and security, lack of authority over data access, issues with data locality and compliance with regulations, and the potential difficulties in recovering data are all key areas where cloud computing impacts digital sovereignty.
To achieve digital sovereignty in the era of cloud computing, organizations must take proactive steps to protect their data. This includes implementing robust security measures, regularly auditing and monitoring access to data, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations, and carefully selecting reliable cloud service providers. It is also essential for organizations to be aware of and understand the legal and regulatory implications of digital sovereignty to avoid significant financial penalties and legal consequences.
