Investors have already made it very obvious how valuable and powerful open source is. According to estimates, EU-based businesses spent close to €1 billion on open-source software (OSS) in 2018, which had between €65 and €95 billion impact on the continent’s economy. This is based on a study about the impact of open-source software and hardware conducted by OpenForum Europe and Fraunhofer ISI.
It is also predicted that such studies’ will serve as the foundation for policy alternatives in numerous digital fields shortly. Long-term, a new open-source policy centered on the EU economy as a whole can be developed using the findings.
In this article, we will provide some of these findings indicating how open-source software contributes to technological independence, competitiveness, and innovation. We will also talk about how this paradigm shift from the earlier conflict between closed and open source foreshadows a new era in which digital companies are constructed utilizing open-source assets.
Couple of Words about OSS
The core principles of open source are adoption, sharing, and cooperation in the development of the code. Moreover, audibility is an important addition to this set of principles since the source code is accessible to everyone and developers can easily look into the codes for security bugs and vulnerabilities.
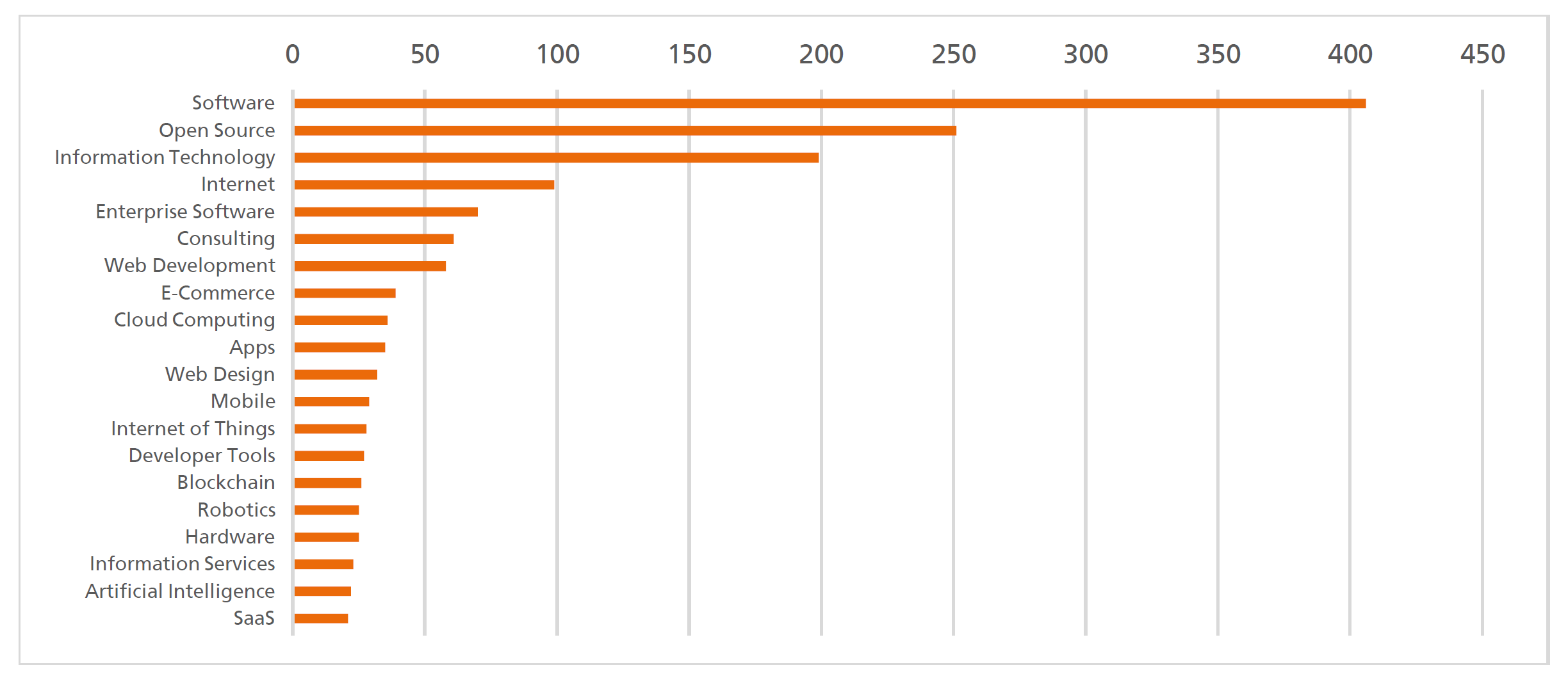
Open source is a mindset for programmers and other free content producers that obviously goes beyond the information technology industry. It is a technology that represents freedom and participation. Software whose source code is open and freely available is referred to as “open source.” As a result, you may modify the software yourself to suit your demands.
OSS struggles for freedom and waging a social solidarity movement. When software is proprietary, it denotes an immoral social structure for its usage and dissemination. In particular, software must abide by four principles in order to be free in
- Usage of the application
- Exploring the code and performing modifications
- Re-distributing the original software
- Re-distributing the modified software
Economical Impact of OSS
The research indicates that an increase of 10% in OSS contributions will yearly produce an additional 0.4% to 0.6% GDP and more than 600 new ICT start-ups in the EU, with an estimated cost-benefit ratio of above 1:4. Case studies show that the public sector might lower total cost of ownership, prevent vendor lock-in, and so strengthen its digital autonomy by purchasing OSS rather than proprietary software. A review of current global and European public policy initiatives is also included in the report.
As said before, according to the report, open-source software generates between €65 and €95 billion in GDP for the European Union and offers the digital economy of the area great room for expansion. The EU should aggressively pursue a shift toward more openness in its political and investment cultures in order to accomplish that.
The research urges the EU to develop an open-source industrial strategy specifically for that purpose and to include it in all of its key policy frameworks, including the European Green Deal and the AI Act. It also suggests establishing a European network of governmental organizations tasked with promoting the use of open technologies, funding open source initiatives and support mechanisms heavily, such as through the flagship Horizon Europe program, which has a budget of €95.5 billion for the year 2021 to 2027 and moving in the open innovation direction in the bloc’s pursuit of digital autonomy.
To put the findings into perspective, the economic worth of open-source software in the EU is similar to the combined value of air and water transportation.
Moreover, these findings are speculated to be increased as the number of open-source-based startups is increasing in the software industry.
Cost-Benefit of Investment in OSS
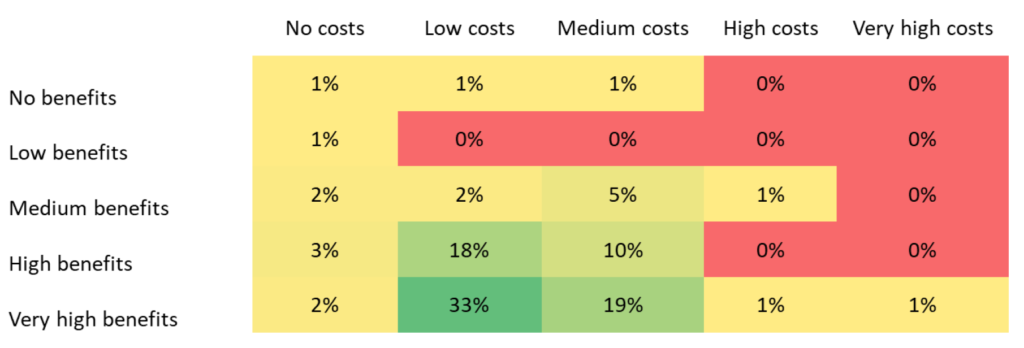
In the survey conducted by OpenForum Europe and Fraunhofer ISI, according to the benefits and cost evaluations, one-third of respondents saw very high benefits and low costs, while more than another third see very high benefits and medium prices or at least high benefits and moderate costs. This shows and potential of OSS as an investment with low cost and high yield.
Open Source as a Public Asset
Over the past 10 years, OSS has entrenched itself in every facet of the software business. In contrast, the above-mentioned report by OpenForum Europe and Fraunhofer ISI indicates that Open-source Hardware (OSH) is now falling behind substantially in terms of development. However, the OSH business landscape is quickly changing. According to the report, OSH might serve as the foundation for the future Internet of Things (IoT), computing, and the digital transformation of the European industry by the end of the digital decade if it experiences the same evolution as OSS.
OSS and Minimizing the Effects of Skills Shortage
OSS can lessen the effects of the skills gap and related issues. Participating in open-source projects may also help businesses and organizations better update the skills of their personnel and retain workers by offering a wider variety of positions. As a result, companies gain benefits from involvement in open-source communities both directly and indirectly. This is because the value that open source generates considerably outweighs the institutional capacity of Europe. Thus, there is tremendous potential for the growth of European institutions and businesses in terms of their institutional capacity for OSS.
Regarding Transparency and Digital Sovereignty
Due to the growing use of digital technology in all spheres of life and business, digital sovereignty is taking on more significance. Information technology is therefore becoming more of strategic concern, particularly for public administrations and how they may translate into policies that go beyond a legislative base and would really have an influence on the entire community, both from a business and citizen standpoint. Open source has the ability to and will play a crucial role in industrial strategy. This is because of the openness, which allows experts to examine the source code and discover any undesired activity or vulnerabilities. However, there is no means to audit the source code for the proprietary program.
Conclusion
The analysis provided by OpenForum Europe and Fraunhofer ISI is indeed a solid foundation to build on according to the European Professional Association for Open Source Software (APELL). Therefore, a step up in terms of political commitment is justified by the necessity for digital sovereignty as well as the numerous beneficial externalities of open-source contributions to the economy. As discussed, if acted upon, OSS has the potential to provide digital sovereignty as well as economical values for the industries that are willing to leverage such a formidable tool.
Achieving digital sovereignty is already the main subject of digital transformation in many companies, especially in the EU with the emergence of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Zextras Carbonio Community Edition as an open-source alternative to proprietary communication and collaboration software is designed to comply with data protection regulations.