Imagine being an IT administrator for a growing enterprise with multiple departments, each requiring different configurations, security policies, and resource allocations. When your company acquires another business, you suddenly need to integrate hundreds more users with different compliance requirements. Without a unified system, you’re facing separate servers, multiple administration consoles, and duplicated updates across isolated environments.
This scenario illustrates why multi-tenancy has become crucial in modern IT architecture. Multi-tenancy refers to an architecture where a single instance of an application serves multiple customer organizations (tenants), with each tenant’s data isolated despite sharing the underlying infrastructure.
Real-World Benefits
Cost Savings: Doing More with Less
Multi-tenancy significantly reduces infrastructure and operational costs by consolidating computing resources. In SaaS environments, shared hardware, storage, and networking enable providers to achieve economies of scale. While exact figures vary, multi-tenant SaaS architectures are broadly recognized for reducing infrastructure and operational costs by consolidating hardware, optimizing energy use, and minimizing administrative overhead. Studies from vendors like NetSuite and Sisense point to substantial cost efficiencies through shared environments and centralized updates.
The public transportation analogy applies well here: single-tenant architectures are like everyone driving their own cars—costly and inefficient. Multi-tenancy resembles a shared bus system, where operational costs are distributed among all users.
Centralized Updates and Reduced Admin Overhead
Multi-tenant systems allow centralized software updates. Administrators can push updates once and apply them across all tenants simultaneously, eliminating version fragmentation and minimizing downtime. This streamlined management reduces repetitive IT labor, with many SaaS providers reporting significant decreases in administrative overhead—freeing up valuable time for innovation and strategic IT initiatives.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Well-implemented multi-tenancy can actually enhance security. Logical data isolation ensures each tenant’s information is compartmentalized, supported by strong authentication, access control, and encryption.
Modern platforms enforce:
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Centralized logging and monitoring
These elements support regulatory standards like HIPAA, GDPR, and SOX, where data governance and auditability are essential.
Scalability Without Growing Pains
Onboarding new tenants in a multi-tenant platform is largely configuration-driven rather than deployment-heavy. For example, organizations have reported reducing onboarding time from multiple weeks to hours by leveraging dynamic tenant provisioning.
Use Cases
Managed Service Providers (MSPs)
MSPs supporting multiple healthcare, finance, or legal clients use multi-tenancy to offer secure, segregated environments on shared infrastructure. This enables them to deliver consistent services while reducing deployment and maintenance complexity.
Educational Institutions
Universities often assign different departments or campuses as separate tenants. Each tenant can have its own domain, policies, and user management, while central IT retains administrative oversight.
Healthcare Networks
Multi-tenancy is vital in healthcare where different clinics or units require isolated data environments. A multi-tenant setup allows central IT to enforce compliance and ensure patient data privacy without duplicating infrastructure.
Compliance and Security in Detail
Carbonio’s multi-tenancy model embraces deep isolation through:
- Row-level database security ensuring data compartmentalization
- RBAC with tenant-scoped permissions to control access
- TLS encryption for data in transit
These capabilities make Carbonio suitable for regulated environments, from healthcare to public sector deployments.
Zextras Carbonio: Designed for Multi-Tenant Excellence
Delegated Administration with Granular Control
Zextras Carbonio features a robust RBAC system, allowing organizations to delegate administrative control by role or scope. For example, a department IT lead can manage users and groups within their tenant, without having access to organization-wide settings. This minimizes risk while enabling operational flexibility.
Role-Based Access Control: Security groups define access permissions for delegated administrators, reducing security risks while maintaining operational flexibility. – read more about it in this article
Full Tenant Isolation
Carbonio supports:
- Custom domains per tenant
- Separate resource quotas
- Independent mail policies and user roles
These isolation layers ensure that tenants are functionally and securely separated, even while sharing the same core infrastructure.
Built-In Compliance Features
With features like Legal Hold, eDiscovery, and audit trails, Carbonio helps IT teams meet regulatory obligations without external tools. These capabilities are built into the core architecture, simplifying governance.
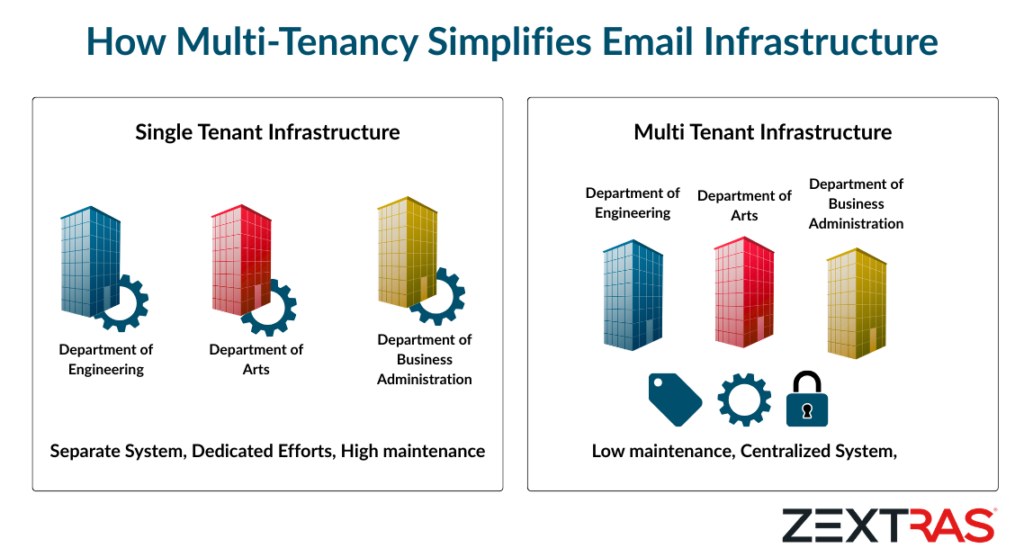
Multi-tenancy is no longer just a technical consideration—it’s a strategic necessity for organizations aiming to scale securely and efficiently. From centralized management and cost savings to tenant-level autonomy and compliance assurance, the advantages are clear.
Platforms like Zextras Carbonio, which are architected from the ground up for secure, scalable multi-tenancy, provide IT teams with the tools they need to manage modern collaboration environments confidently. Whether you’re an MSP, a university, or an enterprise IT leader, adopting multi-tenancy is a smart investment in operational agility and long-term sustainability. If you want to read more on Enhanced Administrative Control and Compliance, check out this article.
